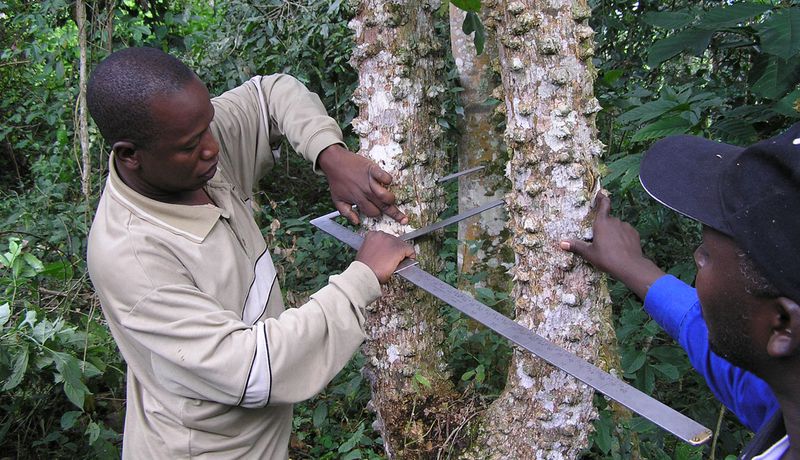
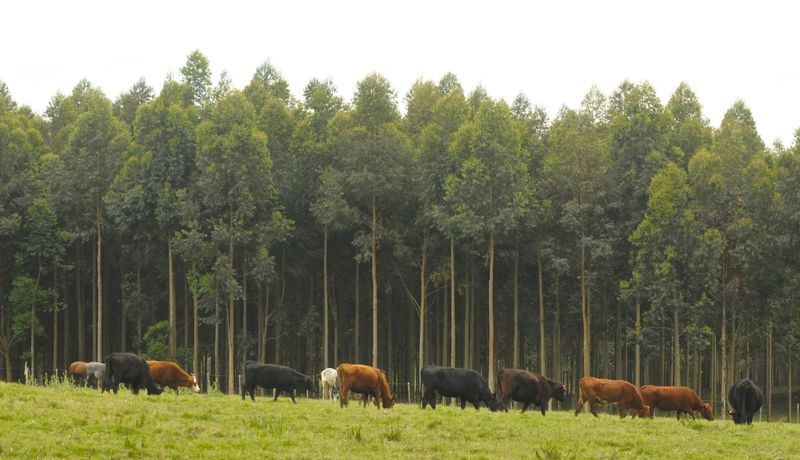
Planting trees is the most easily and widely understood climate solution.
It is fairly easy to plant a tree, but it is much harder to ensure a tree survives to maturity and is monitored to calculate the carbon removed by that tree in its lifetime. The Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) has established a number of innovative ways to properly value trees as more than just timber, afforestation projects being one of those.
To reverse the trend of global tree cover loss, afforestation efforts are critical to restoring our natural world. Afforestation carbon projects offer businesses the opportunity to support areas with degraded land while also offering many social impact co-benefits.
What is afforestation?
Afforestation is the process of establishing a forest in an area where there was no forest before, or not for a long time, usually longer than fifty years ago. It involves planting trees in an area that was previously devoid of forest cover.
Carbon finance is creating incentives to pursue a diverse range of projects like commercial afforestation to create productive forests. These projects focus on establishing and maintaining productive forests on barren lands that were previously without any forest cover for decades.
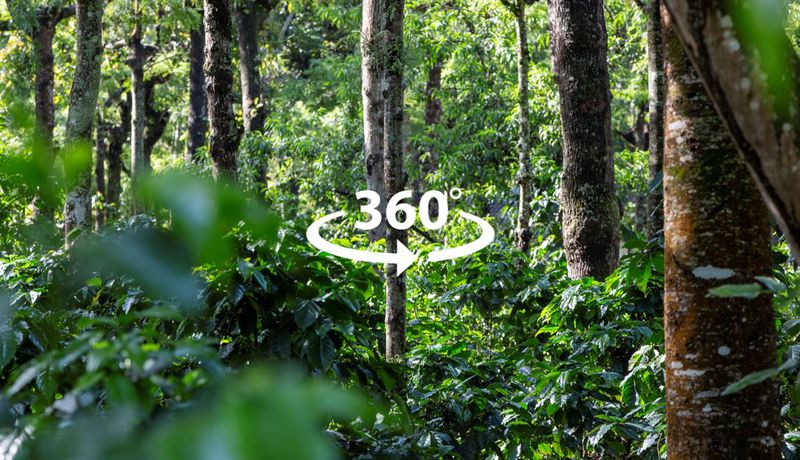
Experience a forestry carbon project
View our immersive 360-degree video tour below to see how some of our global afforestation and reforestation projects are a climate solution that remove carbon and create local job opportunities. You will experience:
- How afforestation and reforestation projects are monitored to calculate the removal (sequestration) of carbon emissions as the trees grow.
- A large-scale commercial forestry project that has found a new way to value trees as more than just the timber they could be cut down for.
- The unique way that latex sap is sustainably harvested from rubber tree forests.
Why is afforestation important to combat climate change?
Afforestation is an important strategy for tackling climate change. As a tree grows, it removes carbon from the atmosphere through the natural process of photosynthesis. Through this same process trees also store large amounts of carbon from the atmosphere in their biomass and in the soil, helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Afforestation also helps to prevent deforestation and forest degradation, which are major sources of CO2 emissions. When forests are cleared for agriculture, pastureland, or other land uses, the carbon stored in the trees is released into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. By establishing new forests through afforestation, we can reduce the pressure on existing forests and help to maintain their carbon storage capacity.
How tree plantations on degraded land contribute to climate action
While it may seem counterintuitive to consider tree plantations that are designed to harvest wood as a form of climate action, sustainably managed plantations are indeed critical. Until the demand for all wood, cardboard, and paper products globally is met by properly managed sustainable forestry projects, primary forests will continue to be at risk. Commercial forestry is therefore needed to protect our remaining old growth forests by acting as a sustainably managed regenerative buffer.
Tree plantations, when planted on barren lands, not only remove carbon as the trees grow but can also improve biodiversity. Of course, a commercial forestry plot will never be as carbon rich or biodiverse as pristine rainforest, but as compared to barren grasslands that have been overgrazed for years with no tree cover, a tree plantation is a huge improvement. Additionally, high-quality wood products used for construction or furniture also count as long-term carbon storage as the carbon in the biomass does not reach the atmosphere until it biodegrades.
In addition to carbon sequestration, afforestation can also have a range of social, economic, and environmental co-benefits, such as
- reducing soil erosion
- protecting watersheds
- providing habitat for biodiversity and
- supporting sustainable livelihoods of those most impacted by climate change but least responsible for it
Afforestation helps increase forest land cover which is much needed in combatting climate change.
What is the process of afforestation?
The process of afforestation typically involves the following steps:
- Site selection: The first step is selecting a suitable site for planting trees. The site should have adequate soil, water, and sunlight to support sustained tree growth.
- Species selection: The next step is to select tree species that are well-suited to the site conditions and the local climate either because they are native to the area, or well-adapted to the local environment.
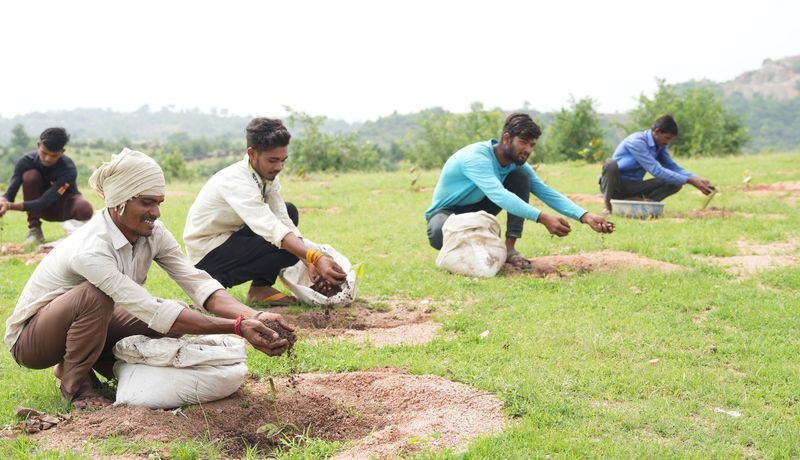
- Planting: After these steps, planting can begin. Depending on the site and the planting method used, trees can be planted by hand, with the use of mechanical equipment, or with the use of aerial seeding.
- Maintenance: After planting, the trees will require ongoing care and maintenance to ensure their survival and growth. This may involve watering, fertilization, weed control, and pest management, among other activities.
- Monitoring: Finally, the trees will need to be monitored over time to assess their growth and development, to identify any issues or challenges that may arise, and to calculate the carbon removed by the trees in their lifetime.
Afforestation is a complex process that requires careful planning, site preparation, and ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure the success of the forest. It is essential that afforestation projects are done to a high standard, in a sustainable way that has passed rigorous quality assurance checks. When done properly, afforestation can provide a range of benefits, including carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable resource use.
How carbon finance helps afforestation projects
Carbon finance can have a significant impact on the success of an afforestation project by providing a reliable revenue source, which ensures the project is sustainable and can be scaled. The sale of high quality carbon credits can generate revenue that can help to cover the costs of establishing and maintaining new forests, which can be costly and require long-term commitments.
Moreover, carbon finance can help to align the goals of afforestation projects with global efforts to mitigate climate change. By generating carbon credits, afforestation projects can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the overall concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This can help to mitigate the effects of climate change and support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Examples of afforestation projects with Climate Impact Partners
Degraded Land Afforestation in Uruguay
The project is certified by the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), balancing timber production and sales with habitat creation. The tree planting project brings new job opportunities to Uruguay, while respecting existing cattle farmers’ land use. The newly grown tree canopy also provides habitat for wildlife.
Carbon finance is used to combine sustainable forestry with cattle grazing. Trees are planted on higher and more degraded land, reducing topsoil degradation, while cattle graze the lower areas. The project promotes sustainable timber creation and contributes to increasing afforestation rates globally.
Community Afforestation India
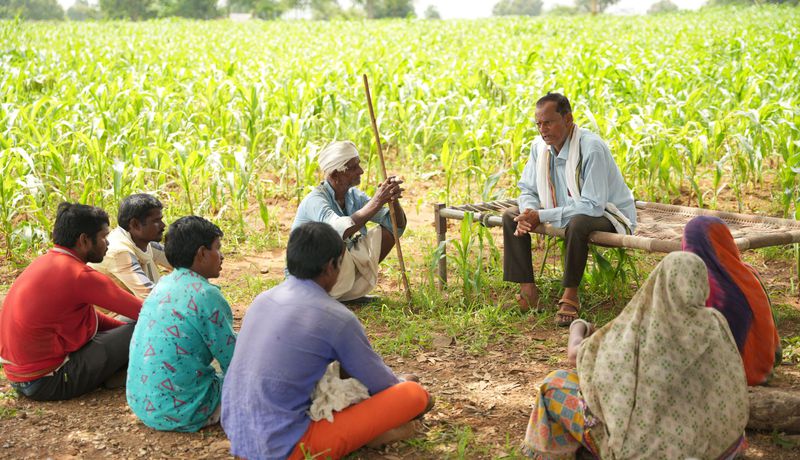
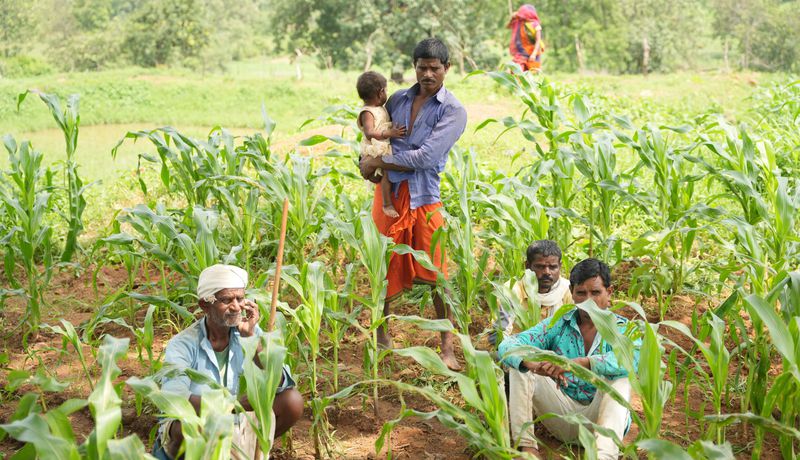
Climate Impact Partners' large-scale tree planting Community Afforestation project in India has been designed for long-term community benefit and water conservation, as well as high integrity nature-based carbon removals. The first year of planting included fruit trees (mango, guava), furniture hardwood trees (teak), medicinal trees (neem) and many other native species.
The project is building resilience in the community through the installation of water conservation infrastructure with community tanks, dams, farm ponds, wells, and solar water pumps, designed to reduce the impact of future droughts for the farmers. The project also helps address gender inequality through involvement of women in farming and reducing time spent collecting water.
Speak with one of our team to learn more about afforestation carbon offset projects and how your company can take climate action today
Verification and validation of forestry carbon projects
All the carbon finance projects we support are independently validated and verified in line with recognized global standards, including the Clean Development Mechanism, the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), the Gold Standard, the American Carbon Registry (ACR) and the Climate Action Reserve (CAR).
Here are some examples of afforestation and reforestation project methodologies used in the Voluntary Carbon Market.
VCS – Verified Carbon Standard:
ACR - American Carbon Registry:
CDM – Clean Development Mechanism: